A healthy diet is important during pregnancy, as a lack of nutrients can affect the child’s health from the very early stages of pregnancy, even before conception.
What to prefer during pregnancy:
- Wholemeal bread and cereals: Because they are high in fiber which helps prevent and fight constipation, contain more vitamins and meet your carbohydrate needs.
- Fruits and vegetables: Because they contain fiber, potassium and water that help against constipation and retention. They even contain folic acid, which is very important especially in the early stages of pregnancy. It is very important to wash fruits and vegetables very well before eating them.
- Meat, poultry and fish: Because they meet the increased needs for protein and Iron, whose deficiency is quite common. Choose fish low in mercury such as sardines, shrimps, anchovies.
- Dairy products or fortified vegetable drinks/yogurts to meet Calcium needs. Prefer hard cheeses such as edamame and pasteurised milk cheeses such as cottage, feta, cream cheese, mozzarella.
- Drink plenty of fluids, especially water (about 2 litres a day)
- Stand in the sun for about 15 minutes daily (not midday if it is summer).
What to avoid during pregnancy:
- Raw and unpasteurised cheeses and milk: Pasteurization kills potentially harmful bacteria.
- Dangerous cheeses: Brie, Roquefort, blue cheese, camembert, camembert
- Raw or undercooked meat: Make sure the meat you eat is very well cooked, meaning there are no traces of blood and the center of the meat is at least 71 degrees Celsius.
- Raw or undercooked eggs: Some foods such as homemade mayonnaise, tiramisu, poached or scrambled eggs can be dangerous.
- Packaged mayonnaise and sauces sold in supermarkets are safe because they are made from pasteurized eggs.
- Raw or undercooked fish and seafood, fish high in mercury: For example, do not consume sushi, sashimi, taramosalata. Even seafood and shellfish that are sold pre-cooked and need to be stored in the refrigerator or freezer. Also avoid swordfish, king mackerel, marlin, fresh tuna and other fish high in mercury.
- Ready-to-eat salads
- Fruit and vegetables outside the home: Because they are not sure they have been washed as much as they should be.
- Liver and liver products: As they contain a lot of Vitamin A, which if accumulated is harmful to you and the fetus.
- Pate foods: because they can contain pathogenic bacteria.
- Canned foods: Canned foods are often coated with bisphenol A, which can have neurological, behavioral, endocrinological effects on infants, and may have been left for quite a long time.
- Alcohol: Not allowed to be consumed at all because alcohol can cross the placenta.
- Caffeine: Up to 200mg per day is allowed.
Supplements:
- It is important to meet the needs for folic acid, especially in the 1st trimester and 1 month before conception, iodine, choline, iron.
- It is recommended to supplement folic acid 0.4 mg per day throughout pregnancy
- Increased Calcium needs, so include 3 dairy products/day and recommendation for safe sun exposure for 15-30 minutes
- Iron needs are at 30mg/day from the beginning of the 12th week and iron supplementation is considered essential.
The caffeine contained in various foods and drinks:
- Filter coffee (e.g. French coffee): 90 mg
- Energy drink: 80 mg in 250 mL
- Single espresso: 60 mg
- Black tea: 50 mg in 220 mL
- Cola: 50 mg in 330 mL
- Dark chocolate: 30 mg in 50 grams
- Milk chocolate: 10 mg in 50 grams
Expected weight gain during pregnancy:

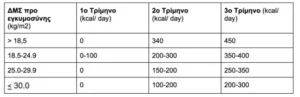
Additional energy needs:
Food safety practices:
1) Cleanliness:
Wash your hands thoroughly with warm water and soap.
Wash your hands before and after handling food, using the bathroom, changing diapers or handling pets.
Wash cutting boards, dishes, utensils and workbenches with warm water and soap.
Rinse raw fruits and vegetables thoroughly under running water.
Avoid eating raw fruits and vegetables from stores, as they may not have been thoroughly washed.
2) Separation:
Separate raw meat, poultry and seafood from ready-to-eat foods.
If possible, use one cutting board for raw meat, poultry and seafood and another for fresh fruit and vegetables.
Place cooked food on a clean plate. If cooked food is placed on an unwashed plate that contained raw meat, poultry or seafood, bacteria from the raw food can contaminate the cooked food.
3) Cooking:
Cook food well. You can even use a food thermometer to check the temperature.
Keep food out of the Danger Zone: The range of temperatures in which bacteria can grow – usually between 4°C and 60°C.
The rule of 2 hours: Discard foods that remain at room temperature for more than 2 hours.
When temperatures are above 32° C, discard food after 1 hour.
4) Refrigeration:
Your refrigerator should register a temperature of 4° C or lower and your freezer -18° C. You can place an appliance thermometer in the refrigerator and check the temperature periodically.
Freeze perishable foods (foods that can be spoiled or contaminated by bacteria if not frozen).
Eat ready-to-eat, perishable foods (dairy, meat, poultry, seafood, produce) as soon as possible.

Sources:
- FDA: Food Safety for Mom to Be A-a-Glance
- eufic:Healthy pregnancy: foods to avoid when pregnant
- eufic: A healthy way through pregnancy
- Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines.
- Mayo Clinic:Pregnancy week by week
- Nutrition Recommendations in Pregnancy and Lactation
- Nutrient Requirements during Pregnancy and Lactation
- People at Risk: Pregnant Women

